SSH Remote IoT Device Free Download: Your Guide To Easy Access In 2024
Connecting to your smart gadgets from a distance can seem like a puzzle, yet it does not have to be a big problem. Many folks want to reach their little devices, like home automation hubs or tiny computers, without being right next to them. This desire often comes with a wish for tools that do not cost anything. We will look at how you can get your smart devices to talk to you, even when you are far away, using a very common and quite helpful way to connect: SSH.
For anyone with an IoT device, whether it is a tiny sensor or a home assistant, the idea of checking in on it or making changes from anywhere feels pretty neat. You might have a Raspberry Pi running a weather station in your backyard, or perhaps a smart switch in another room that needs a quick tweak. Being able to access these without physically going to them, and doing it without spending extra cash on special software, is something many people look for. This article shows you how to do just that, using methods that are generally available.
This approach, which many people use for remote connections, offers a direct path to your devices. It is, you know, a way to send commands and get information back, making it feel like you are sitting right there. We will talk about how this connection works, some of the free things you might need, and what to do if things do not quite work out the first time. It is all about making your remote device management a whole lot simpler, and honestly, a lot more possible.
- Adam Lz Nicole Divorce
- Arthur Ferrari Ex De Flávia Alessandra
- Toor Pekai Yousafzai
- Tereza Love Bio
- Mr Fapello
Table of Contents
- What is SSH and Why It Matters for Your IoT Devices
- Getting Started with SSH: Free Tools You Can Use
- Setting Up SSH on Your IoT Device
- Common Challenges and How to Handle Them
- Keeping Your IoT SSH Connections Safe
- The Benefits of Remote IoT Access
- Looking Ahead for IoT and SSH
What is SSH and Why It Matters for Your IoT Devices
When we talk about reaching a computer or a device that is somewhere else, SSH often comes up. It is a very common way to do things like that, so it is kind of like a secret passage for your commands and data. For your little smart devices, this method is a really big deal, because it lets you talk to them directly, even if they are across the room or across the country. It is, you know, a standard way to make sure your remote chat is private.
The Basics of SSH
SSH stands for Secure Shell. Think of it as a secure tunnel you can create between your computer and another machine, like your IoT device. Through this tunnel, you can send commands, move files, and even run programs on the remote device, all while keeping your information private. It uses, like, special codes to make sure no one else can listen in on your conversation. So, you are connecting via the SSH protocol, as indicated by the `ssh://` prefix on your clone URL, if you have ever seen that.
This system works by making sure both sides of the connection trust each other. Using SSH, every host has a key, which is like a unique fingerprint. Your computer, the client, remembers the host key associated with a particular device. This helps make sure you are connecting to the right device and not, say, a tricky imposter. It is, you know, a simple way to confirm who you are talking to.
- Jonathan Cahn Wedding
- Macron Children Ages
- Check Vanillagift Balance
- Who Is Gayle Kings Current Husband
- Johnny Sins Child Name
Why IoT Devices Love SSH
IoT devices are often small, without a screen or keyboard, and they might be placed in hard-to-reach spots. SSH gives you a way to control them without needing to plug in a monitor or move them. You can check their status, update their software, or fix problems, all from your own computer. This makes managing a whole bunch of smart gadgets much, much easier. It is, you know, a pretty efficient way to handle things.
Getting Started with SSH: Free Tools You Can Use
To start talking to your IoT devices using SSH, you will need a piece of software on your own computer. Good news, there are many free options out there that do the job perfectly well. You do not have to buy anything special to begin. These tools are, like, readily available for almost anyone to pick up and use.
Choosing Your SSH Client
If you use a computer with Linux or macOS, you already have an SSH client built right in. You just open your terminal or command prompt, and it is ready to go. For Windows users, things used to be a little different, but now Windows 10 and 11 often come with an OpenSSH client already installed. If yours does not, or if you prefer a different tool, PuTTY is a very popular free option that has been around for ages. It is, you know, a simple program to get.
How to Get Them
For Linux or macOS, just open your terminal. That is it! For Windows, you can check if OpenSSH is installed by typing `ssh` into your Command Prompt or PowerShell. If it is not there, you can add it through Windows Features, or download PuTTY from its official website. It is a pretty straightforward download, and the setup is usually quick. You know, it is just a simple install.
Setting Up SSH on Your IoT Device
Before you can connect from your computer, your IoT device needs to be ready to receive SSH connections. This usually involves a few simple steps, depending on the type of device you have. Most small Linux-based devices, like Raspberry Pis, make this pretty easy. It is, like, a common first step for many projects.
Initial Device Setup
First, make sure your IoT device is connected to your local network. This might mean plugging it into your router with a cable or connecting it to your Wi-Fi. You will also need to know its IP address on your network. There are many ways to find this, like checking your router's connected devices list or using network scanning tools. It is, you know, a basic step to get things going.
Enabling SSH on the Device
For many IoT operating systems, SSH might be turned off by default for security reasons. You will usually need to enable it. For a Raspberry Pi running Raspberry Pi OS, you can do this through the `raspi-config` tool or by placing an empty file named `ssh` (no extension) into the boot partition of the SD card before you even start the device. Once it boots, SSH should be active. This is, like, a pretty common way to get it going.
Once SSH is on, you can try to connect from your computer. You would use a command like `ssh username@ip_address_of_device`. For example, if your Raspberry Pi's username is `pi` and its IP is `192.168.1.100`, you would type `ssh pi@192.168.1.100`. The first time you connect, you might get a message about the host's key, which you should accept. It is, you know, a standard part of the first connection.
Common Challenges and How to Handle Them
Sometimes, things do not go perfectly smoothly when you are trying to get SSH to work. I have had my own share of head-scratching moments, like when SSH stopped working after installing GitLab, even though it was fine before. These little hiccups are pretty common, and there are ways to sort them out. It is, like, part of the process for many people.
Trouble After Installing Other Programs
I remember a time when I installed GitLab on my server, and suddenly my SSH connections stopped working correctly. Before that, everything was fine. This can happen if a new program changes network settings or messes with SSH configurations. If you run into this, it is good to check recent changes you made. You might need to restart SSH services or even look at your firewall settings. It is, you know, a common side effect of adding new things.
Understanding Host Keys
As mentioned, using SSH, every host has a key. Your client computer remembers the host key associated with a particular device. If that device's key changes (maybe you reinstalled its operating system), your computer will give you a warning. It might say something about a "remote host identification has changed." To fix this, you usually need to remove the old key from your `known_hosts` file on your computer. You can find commands for this online, or you might get a hint right in the error message. It is, you know, a safety feature that can sometimes be a bit of a bother.
Making Your SSH Keys Stick
If you use SSH keys for password-less login, you might find yourself typing your passphrase every time you connect. To avoid this, you can add your identity using a tool like `ssh-agent` or `keychain`. As someone pointed out in the comments of a guide I was following, using `keychain` helps to persist your keys, so you do not have to add them again after every reboot. This is, you know, a very handy trick for daily use.
To use your SSH key with services like GitHub or GitLab, you need to copy your public key. I remember doing this after installing Git on a new work computer. You typically use a command like `pbcopy < ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub` (on macOS) or `cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub | clip` (on Windows) to copy the key to your clipboard. Then, you paste it into the SSH key settings on your GitHub or GitLab account. It is, you know, a simple way to get your key where it needs to go.
X11 Forwarding and Display Issues
Sometimes you want to run a graphical program on your remote IoT device and see its window on your local computer. This is called X11 forwarding. If you run SSH and the display is not set, it means SSH is not forwarding the X11 connection. To confirm that SSH is forwarding X11, you can check for a line containing "requesting X11 forwarding" in your SSH client's output when you connect with the `-X` option. If it is not working, you might need to install X11 server software on your local machine or check SSH server configuration on the IoT device. It is, you know, a bit more advanced but very useful.
Copying Files and Folders
I often use SSH to connect to a remote machine, and then I need to copy files or even an entire directory. There is a way to do this from your local machine to the remote machine, and vice-versa. The `scp` command (Secure Copy) is your friend here. For example, to copy a file from your local machine to your IoT device, you might use `scp /path/to/local/file username@ip_address:/path/to/remote/destination`. I found a link once to do it the other way around, copying from remote to local, and it is just as straightforward. It is, you know, a very common task.
To copy an entire directory, you would add the `-r` option for recursive copying. So, `scp -r /path/to/local/folder username@ip_address:/path/to/remote/destination` would do the trick. This is super handy for moving logs, configuration files, or even entire project folders to or from your IoT devices. It is, like, a simple yet powerful command.
Keeping Your IoT SSH Connections Safe
While SSH is built for security, how you set it up really matters, especially for IoT devices that might be out in the open. You want to make sure your remote access is not a backdoor for others. This is, you know, a big part of using these tools responsibly.
Strong Passwords and Key Pairs
Always use very strong, unique passwords for your IoT devices. Even better, consider using SSH key pairs instead of passwords for login. This means you have a private key on your computer and a public key on the IoT device. It is generally much safer than relying on passwords alone, as keys are much harder to guess. It is, you know, a more secure way to get in.
You can generate an SSH key pair on your computer using a command like `ssh-keygen`. It will create two files: `id_rsa` (your private key) and `id_rsa.pub` (your public key). You then copy the public key to your IoT device's `~/.ssh/authorized_keys` file. This lets you log in without a password, just by having the correct private key. It is, like, a pretty standard security practice.
Regular Updates
Keep the software on your IoT devices updated, including the SSH server. Updates often fix security holes that bad actors could try to use. Make it a habit to check for and apply updates regularly. This is, you know, a simple step that makes a big difference.
Consider changing the default SSH port (which is 22) on your IoT device to a different, less common port. This does not make it completely secure, but it does make it less likely for automated scanning tools to find your SSH service. It is, you know, a little extra layer of caution.
The Benefits of Remote IoT Access
Having SSH access to your IoT devices brings a lot of good things. You can monitor them from anywhere, troubleshoot issues without being physically present, and even automate tasks. If you have a fleet of devices, this capability saves a lot of time and effort. It is, like, a huge convenience for many people.
Imagine your smart garden system needing a quick check on its sensor readings, or your home server requiring a software update while you are away. With SSH, you can do all this from your phone or laptop. This level of control makes managing your connected world much more fluid. You know, it just makes things easier.
You can learn more about connecting to devices on our site, and find out about other remote access methods we discuss. These resources offer even more ideas for how to keep your systems running smoothly.
Looking Ahead for IoT and SSH
The number of smart devices around us is just growing and growing in 2024, and this trend is not slowing down. As more things get connected, the need for simple, secure ways to manage them from afar becomes even more important. SSH, with its long history of being reliable, will probably stay a key tool for a long time. It is, you know, a pretty foundational piece of technology.
New ways of making SSH even easier to use, perhaps with simpler setup processes or better ways to manage many devices at once, might appear. But the basic idea of a secure, direct connection will likely stay the same. Keeping up with these developments will help you get the most out of your IoT setup. It is, like, a good idea to stay informed.
For more detailed information on SSH protocols and their workings, you might find it helpful to look at resources from organizations like the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), which helps set the standards for internet technologies. Their publications offer a deeper look into how these systems are built. You know, it is a good place for more technical stuff.
People Also Ask
How do I SSH into an IoT device?
To SSH into an IoT device, you first need to make sure SSH is turned on on the device itself, which often involves a setting or a special file. Then, from your computer, you open a terminal or command prompt and use the command `ssh username@device_ip_address`. For example, `ssh pi@192.168.1.100`. The first time, you might need to accept the device's host key. It is, you know, a direct way to connect.
Is SSH secure for IoT?
SSH is generally considered quite secure for IoT devices because it encrypts all traffic, meaning your commands and data are private. However, its security really depends on how you use it. Using strong passwords, setting up SSH key pairs instead of just passwords, and keeping your device's software updated are all very important steps to keep your connections safe. It is, like, a good tool when used carefully.
What free tools are available for remote IoT access?
For remote IoT access using SSH, the most common free tool is the SSH client built into Linux and macOS operating systems, which you can use directly from the terminal. For Windows users, the OpenSSH client is often included in newer versions, or you can download PuTTY, which is a very popular and free SSH client. These tools are, you know, pretty much all you need to get started.
- Asap Rocky And Travis Scott
- Who Is Robert Plants Partner Now
- Hailey Bieber Dad
- Michael Mckean
- Fernando Moreira Salles
Remote IoT Monitoring On Android: Free Download & SSH Guide
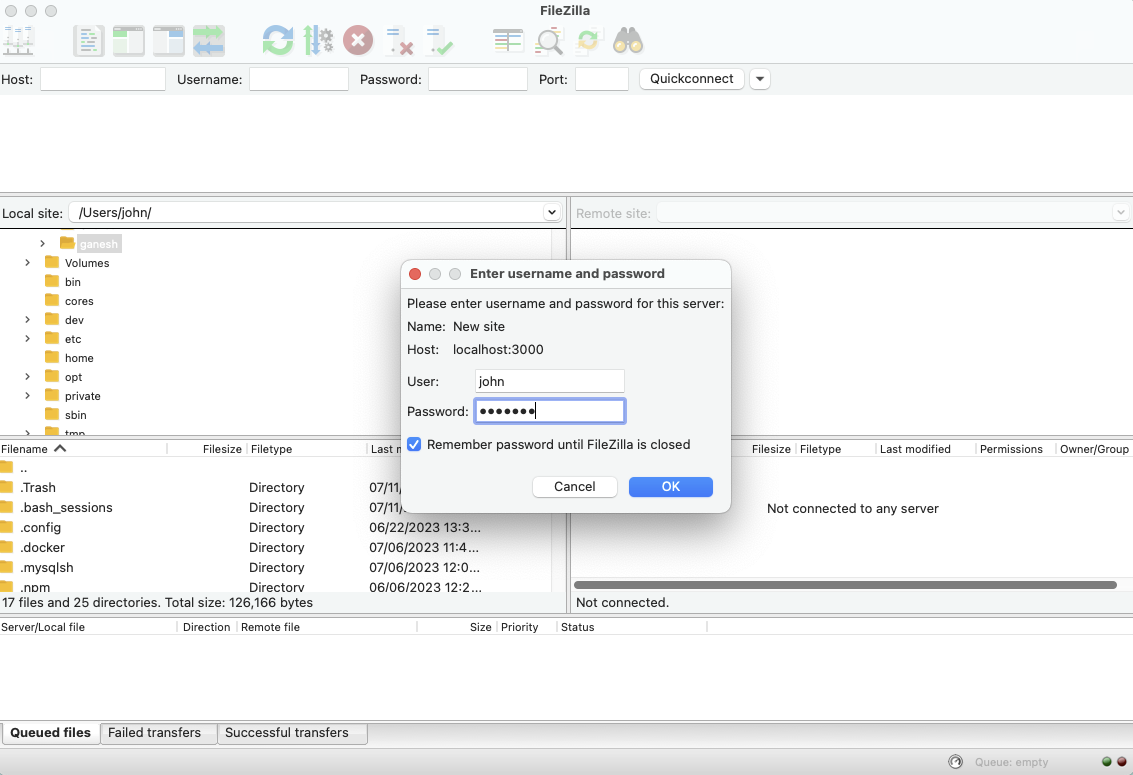
IoT SSH Remote Access - SocketXP Documentation
SSH Remote IoT Device Android: A Comprehensive Guide