SSH IoT Device Management AWS: Securely Controlling Your Connected World
Are you looking to keep your Internet of Things (IoT) devices running smoothly, even when they're tucked away behind tricky firewalls or spread across vast distances? Managing these gadgets, especially when you're dealing with a large number of them, can, in a way, feel like a real puzzle. But there's good news! Combining the trusted security of SSH (Secure Shell) with the amazing reach of AWS (Amazon Web Services) offers a truly effective way to take charge of your IoT setup.
The Internet of Things, you know, just keeps getting bigger, bringing us everything from smart home gadgets to complex industrial sensors. With this growth, the need for safe and simple ways to reach and manage these devices from afar becomes, frankly, super important. This is where the combination of SSH and AWS IoT Device Management really shines. It helps you keep things running without a hitch and makes everything much more secure, which is pretty neat.
So, how do you make sure your devices are always accessible for updates, fixes, or just a quick check-in, no matter where they are? That's what we're going to explore today. We'll look at how SSH, a protocol many of us already rely on for secure connections, teams up with AWS's powerful tools to give you that control. It's about having the ability to manage your connected world with confidence, even when devices are deployed behind restricted firewalls at remote sites, which, as a matter of fact, is a common challenge.
- Whitney Wren Nudes Leaked
- Kyle Larson Net Worth
- How Old Is Sza Daughter
- How Old Zahide
- صوفي راين ويكيبيديا
Table of Contents
- What is SSH for IoT Management?
- Why AWS IoT Device Management is Your Ally
- The Magic of AWS IoT Secure Tunneling
- Setting Up Your SSH IoT Connection on AWS
- Common Scenarios and Troubleshooting Tips
- Beyond Basic SSH: Advanced Uses
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Bringing It All Together
What is SSH for IoT Management?
SSH, or Secure Shell, is basically a cryptographic network protocol. It's made to let devices talk to each other safely over networks that might not be so secure. When you think about managing IoT devices, SSH is, in some respects, a very handy tool. It lets you get a command-line interface to your remote devices, which means you can run commands, transfer files, and even set up secure tunnels for other services.
For example, you might have a situation where you need to check a log file on an IoT sensor out in the field. Instead of physically going there, you can use SSH to connect and, you know, just peek at the logs. This ability to connect and control from afar is, quite frankly, a cornerstone of modern technological progress, especially with so many devices spread out. It's a bit like having a remote control for your entire fleet of gadgets.
The beauty of SSH is its security features. Every host, apparently, has a key, and clients remember the host key associated with a particular server. This helps make sure you're connecting to the right device and not some imposter. This secure connection is, obviously, super important when you're dealing with sensitive data or critical operations on your IoT devices.
- Mbti Barack Obama
- Yungblud And Billie Eilish
- Do Adam Sandlers Daughters Play In Happy Gilmore 2
- Anna Ralphs Porn Bio
- Daughter Of A Governor Model
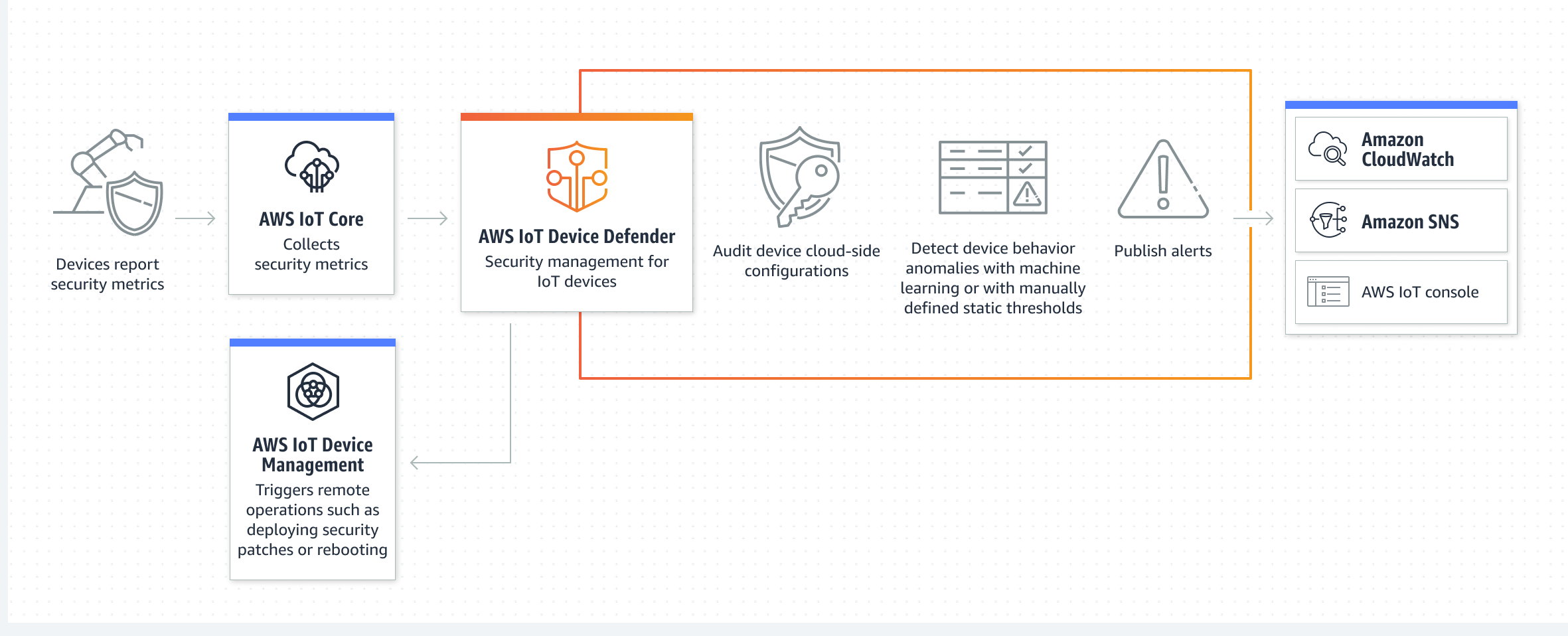
Why AWS IoT Device Management is Your Ally
AWS IoT Device Management provides a whole bunch of tools that help businesses build IoT applications for just about any industry. It's not just about connecting devices; it's about making sure they're onboarded properly, managed efficiently, and kept secure throughout their life. When you combine this powerful AWS infrastructure with SSH, it, frankly, becomes a very powerful way to manage your IoT devices, making sure everything runs smoothly and safely.
One of the biggest challenges with IoT devices is, you know, getting them connected and keeping them updated, especially when they're behind firewalls. AWS IoT Device Management helps with this by letting customers onboard new devices. You can use the AWS IoT console or an API to upload templates that you fill with information about your devices. This streamlines the whole process, which is pretty convenient.
Moreover, AWS IoT Device Management offers a feature called Device Tunneling. This is specifically for creating secure remote SSH sessions to devices that are, say, behind restricted firewalls. So, if you've got devices in a factory or a remote location where direct access is blocked, AWS IoT Device Management, basically, gives you a way in. It’s a very clever solution for a common problem, making sure you can troubleshoot or update devices without needing to be on-site.
The Magic of AWS IoT Secure Tunneling
AWS IoT Secure Tunneling is, in a way, the real star when it comes to SSH IoT device management on AWS. It helps customers set up two-way communication to remote devices that are sitting behind a firewall. This connection is managed by AWS IoT, making it secure and reliable. It means you can reach those devices for things like troubleshooting, sending configuration updates, or doing other operational tasks.
Consider a situation where you've had trouble with SSH not working after certain installations, perhaps because of port conflicts or configuration changes, much like how a GitLab installation might affect local SSH. AWS IoT Secure Tunneling helps bypass these common network hurdles by creating a secure tunnel. This means you don't have to worry about opening specific ports on your firewall for direct SSH access, which is a significant security improvement.
How Secure Tunneling Works
The way AWS IoT Secure Tunneling works is, frankly, quite ingenious. When you need to connect to a device, you create a tunnel through the AWS IoT console or its API. This tunnel acts as a secure pathway between your local machine and the remote IoT device. It's a bit like building a private, secure bridge over a busy, public road.
Once the tunnel is active, you can then use your standard SSH client to connect through this secure pathway. The traffic, you know, flows through the tunnel, which is encrypted and managed by AWS IoT. This means your SSH session is protected from snooping or interference, even if the underlying network is, apparently, not secure. It's a very robust way to ensure your remote operations are private and safe.
This process also means that your IoT device doesn't need to have a publicly accessible IP address or open inbound ports. It just needs to be able to connect outbound to AWS IoT, which is a much safer network configuration. This is, basically, a game-changer for devices deployed in restricted environments, making remote access possible where it once was not, which is pretty cool.
Creating Your First Tunnel
Setting up a tunnel is, actually, quite straightforward. From the AWS IoT console, you can create a tunnel either from the tunnels hub or directly from the details page of an IoT thing you've already made. When you create a tunnel from the tunnels hub, you can, you know, specify the source and destination details.
You'll need to define which device is the "destination" (your IoT device) and which entity is the "source" (your local machine or a jump host). AWS then gives you unique client access tokens for both ends of the tunnel. You use these tokens with a local proxy client on your machine and a secure tunneling agent on your IoT device to establish the connection. This setup is, arguably, very flexible and allows for precise control over who can connect to what.
Once the tunnel is established, you can, you know, just run your SSH command as usual, but instead of connecting directly to the device's IP, you'll connect to a local port that the proxy client is listening on. This local port then forwards your SSH traffic through the secure tunnel to your IoT device. It's a seamless experience once it's set up, making remote management feel almost like you're right there with the device.
Setting Up Your SSH IoT Connection on AWS
Getting your SSH IoT connection ready on AWS involves a few key steps. It's not just about creating a tunnel; it's also about preparing your devices and managing your SSH keys properly. This part is, frankly, very important for ensuring secure and reliable access, much like how generating your SSH key and adding it to GitLab is crucial for cloning projects.
You'll want to make sure your IoT device has an SSH server running and that it's configured to accept connections. This might involve installing an SSH daemon if it's not already there. For example, if you're using a server running Ubuntu, you'd make sure OpenSSH is installed and running. This foundational step is, basically, what allows the secure tunnel to actually carry your SSH session.
Device Preparation and Configuration
Before you can SSH into your IoT device through AWS, the device itself needs to be ready. This means it should have an operating system that supports SSH, like a Linux distribution, and the SSH server software needs to be installed and running. You'll also need to make sure the device can connect outbound to the AWS IoT service endpoints to establish the secure tunnel.
Configuration on the device often involves setting up a user account for SSH access and, crucially, configuring it to use SSH keys instead of passwords. This is a much more secure practice, especially for devices that are out in the field. Think about how you might need to connect to a SSH proxy server using a specific keypair; the same principle applies here for your IoT devices. This step is, arguably, one of the most important for security.
You might also need to install a secure tunneling agent on your IoT device. This agent is a small piece of software that communicates with AWS IoT Secure Tunneling and handles the device side of the tunnel connection. It's what allows the device to, you know, participate in the secure communication. This agent needs to be configured with the device's unique client access token from AWS, which it uses to authenticate and establish its end of the tunnel.
Managing SSH Keys for IoT Devices
Proper SSH key management is, frankly, non-negotiable for secure IoT device access. Instead of passwords, which can be guessed or brute-forced, SSH keys provide a much stronger form of authentication. You'll generate a public/private key pair. The public key goes on your IoT device, and you keep the private key secure on your local machine.
When you're dealing with many devices, managing individual keys can become, you know, a bit of a chore. However, tools and practices exist to help streamline this. For instance, you might use a configuration management system to push public keys to your devices. It's a bit like how you'd add your SSH key to GitLab after generating it on a new work computer; the principle of distributing the public key is similar.
It's also a good idea to use specific keypairs for specific purposes, rather than your default `id_rsa` keypair. This enhances security by limiting the scope of any compromised key. If you need to connect to a SSH proxy server using a keypair created specifically for it, you know, that's a very good security practice to extend to your IoT fleet as well. Regularly rotating keys is also a wise practice, ensuring that even if a key is compromised, its window of vulnerability is limited.
Common Scenarios and Troubleshooting Tips
Even with the best setup, you might run into situations where SSH isn't working as expected. This can be, you know, a bit frustrating, especially when you're trying to manage devices remotely. One common scenario is when you've just made a change, like updating a system or installing new software, and suddenly SSH access seems to stop. This is a bit like when SSH stopped working for me after installing GitLab, or after I changed my Apple ID password and restarted my Mac.
When you're troubleshooting, first, check the basics. Is the device actually online and connected to the internet? Can it reach AWS IoT endpoints? Sometimes, the simplest things are, frankly, the cause of the problem. You might need to check network configurations on the device or ensure its secure tunneling agent is running correctly.
If you're having trouble connecting, try to get more diagnostic information. For example, if you're trying to use X11 forwarding and it's not working, you'd check for a line containing "requesting X11 forwarding" in your SSH client's output. This kind of detailed checking can, obviously, point you toward the exact issue. Similarly, if a `git pull origin master` gives an error, the output often hints at SSH protocol issues, as indicated by the `ssh://` prefix on the clone URL, so reading error messages carefully is very helpful.
Another common issue involves permissions or incorrect key configurations. Double-check that the public key on the IoT device matches the private key you're using. Make sure the permissions on your private key file are correct (usually `chmod 400`). Sometimes, a simple command to fix repository issues, like one taken from Git's documentation, can be adapted to resolve SSH key problems on your device, which is pretty handy.
Remember that when devices are deployed behind restricted firewalls at remote sites, you need a way to gain access for troubleshooting and updates. AWS IoT Secure Tunneling is designed to solve this specific problem. If your tunnel isn't forming, check the AWS IoT console for tunnel status and any error messages. It's a bit like how my server was always connected and worked properly when I was in the workplace; you want that same reliability for your remote IoT devices, and troubleshooting steps should aim to restore that.
Beyond Basic SSH: Advanced Uses
SSH offers more than just a simple command-line shell. For IoT device management on AWS, you can use SSH for a variety of advanced tasks. One powerful use is SSH tunneling for other services. For example, if you have a PostgreSQL database running on an IoT device or a local server (like PostgreSQL 9.3 on Ubuntu Server 14.04), and you want to connect to it securely from your local machine, you can create an SSH tunnel.
This is a bit like how you might SSH into a server via terminal to connect with `psql`, but then struggle to configure a remote client like pgAdmin III directly. An SSH tunnel, created through AWS IoT Secure Tunneling, allows you to forward a local port on your machine to the remote database port on your IoT device. This means your pgAdmin III client can connect to `localhost:your_local_port`, and the traffic, you know, goes securely through the tunnel to the remote database. It's a very effective way to manage services on your devices without exposing them directly to the internet.
You can also use SSH for file transfers with `scp` or `sftp`. This is incredibly useful for pushing firmware updates, configuration files, or pulling log data from your devices. Automating these tasks with scripts, perhaps using Python to call command-line commands like `ssh` or `scp`, can save a lot of time and reduce manual errors, especially when managing a large fleet of devices. It's a bit like writing a script to automate command line commands in Python, which is a common practice for efficiency.
Furthermore, SSH can be used for port forwarding, which allows you to access other services running on your IoT device's local network, assuming your device can act as a jump host. This opens up possibilities for more complex remote diagnostics and management, which, frankly, expands the utility of your SSH connection beyond just the device itself.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions folks often have about managing IoT devices with SSH on AWS:
Can you remotely access and manage your Internet of Things (IoT) devices securely, regardless of their location and the firewalls they may be behind?
Yes, absolutely! AWS IoT Secure Tunneling is specifically designed to help you do just that. It creates a secure, bidirectional connection to your devices, even when they are located behind restricted firewalls at remote sites, making remote management very possible and safe.
What is the main benefit of using SSH with AWS IoT Device Management?
The biggest benefit is gaining secure, remote access to your IoT devices for operational tasks like troubleshooting, configuration updates, and software deployments. This combination, you know, ensures seamless operations and enhanced security, letting you manage devices efficiently no matter where they are, which is pretty handy.
How does AWS IoT Secure Tunneling handle device security?
AWS IoT Secure Tunneling helps keep your devices safe by not requiring them to have publicly exposed ports or IP addresses. All communication happens over a secure, encrypted tunnel managed by AWS IoT. This means your SSH sessions are protected, and the attack surface on your devices is significantly reduced, which is a very good thing for overall security.
Bringing It All Together
Managing IoT devices effectively is, frankly, a big part of modern tech progress. And combining AWS IoT with SSH can really make device security and operations much better. We've seen how SSH, a protocol many of us already use and trust, becomes a very powerful tool for IoT device management when it's paired with AWS's strong infrastructure. As the Internet of Things continues to grow, securely reaching IoT devices through SSH on AWS has, obviously, become a very important part of managing modern cloud setups.
AWS IoT Secure Tunneling, in particular, helps create safe tunnels to your IoT devices, letting you do remote operations using SSH. This is super helpful when your devices are stuck behind firewalls, making it possible to access them for troubleshooting or updates. It's a bit like having a direct, secure line to every single one of your gadgets, no matter how far away they are. So, for anyone working with connected devices, exploring these tools is, basically, a very smart move.
To learn more about SSH IoT device management on our site, and to explore other ways to keep your connected world running smoothly, be sure to check out AWS IoT Device Management's secure tunneling features. This approach really helps you stay in control, ensuring your IoT solutions are not just innovative but also very secure and manageable, which, as a matter of fact, is what everyone wants.
- Ari Fletcher Baby Father
- How Long Was Roseanne Married To Tom Arnold
- Brad Pitt Movie Where He Is A Gypsy
- Avshara Ray
- Disco Dti Outfits

AWS IoT Device Management Features - AWS

AWS IoT Device Management Features - AWS
Securing IoT Devices - AWS IoT Device Defender - AWS